

The Tool Box needs your help
to remain available.
Your contribution can help change lives.
Donate now.

Seeking supports for evaluation?
Learn more.
| Learn how program evaluation makes it easier for everyone involved in community health and development work to evaluate their efforts. |
This section is adapted from the article "Recommended Framework for Program Evaluation in Public Health Practice," by Bobby Milstein, Scott Wetterhall, and the CDC Evaluation Working Group.
Around the world, there exist many programs and interventions developed to improve conditions in local communities. Communities come together to reduce the level of violence that exists, to work for safe, affordable housing for everyone, or to help more students do well in school, to give just a few examples.
But how do we know whether these programs are working? If they are not effective, and even if they are, how can we improve them to make them better for local communities? And finally, how can an organization make intelligent choices about which promising programs are likely to work best in their community?
Over the past years, there has been a growing trend towards the better use of evaluation to understand and improve practice.The systematic use of evaluation has solved many problems and helped countless community-based organizations do what they do better.
Despite an increased understanding of the need for - and the use of - evaluation, however, a basic agreed-upon framework for program evaluation has been lacking. In 1997, scientists at the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recognized the need to develop such a framework. As a result of this, the CDC assembled an Evaluation Working Group comprised of experts in the fields of public health and evaluation. Members were asked to develop a framework that summarizes and organizes the basic elements of program evaluation. This Community Tool Box section describes the framework resulting from the Working Group's efforts.
Before we begin, however, we'd like to offer some definitions of terms that we will use throughout this section.
By evaluation, we mean the systematic investigation of the merit, worth, or significance of an object or effort. Evaluation practice has changed dramatically during the past three decades - new methods and approaches have been developed and it is now used for increasingly diverse projects and audiences.
Throughout this section, the term program is used to describe the object or effort that is being evaluated. It may apply to any action with the goal of improving outcomes for whole communities, for more specific sectors (e.g., schools, work places), or for sub-groups (e.g., youth, people experiencing violence or HIV/AIDS). This definition is meant to be very broad.
Examples of different types of programs include:
Program evaluation - the type of evaluation discussed in this section - is an essential organizational practice for all types of community health and development work. It is a way to evaluate the specific projects and activities community groups may take part in, rather than to evaluate an entire organization or comprehensive community initiative.
Stakeholders refer to those who care about the program or effort. These may include those presumed to benefit (e.g., children and their parents or guardians), those with particular influence (e.g., elected or appointed officials), and those who might support the effort (i.e., potential allies) or oppose it (i.e., potential opponents). Key questions in thinking about stakeholders are: Who cares? What do they care about?
This section presents a framework that promotes a common understanding of program evaluation. The overall goal is to make it easier for everyone involved in community health and development work to evaluate their efforts.
The type of evaluation we talk about in this section can be closely tied to everyday program operations. Our emphasis is on practical, ongoing evaluation that involves program staff, community members, and other stakeholders, not just evaluation experts. This type of evaluation offers many advantages for community health and development professionals.
For example, it complements program management by:
It's important to remember, too, that evaluation is not a new activity for those of us working to improve our communities. In fact, we assess the merit of our work all the time when we ask questions, consult partners, make assessments based on feedback, and then use those judgments to improve our work. When the stakes are low, this type of informal evaluation might be enough. However, when the stakes are raised - when a good deal of time or money is involved, or when many people may be affected - then it may make sense for your organization to use evaluation procedures that are more formal, visible, and justifiable.
To clarify the meaning of each, let's look at some of the answers for Drive Smart, a hypothetical program begun to stop drunk driving.
The following framework provides an organized approach to answer these questions.
Program evaluation offers a way to understand and improve community health and development practice using methods that are useful, feasible, proper, and accurate. The framework described below is a practical non-prescriptive tool that summarizes in a logical order the important elements of program evaluation.
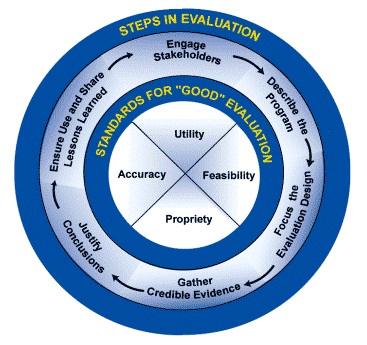
The six connected steps of the framework are actions that should be a part of any evaluation. Although in practice the steps may be encountered out of order, it will usually make sense to follow them in the recommended sequence. That's because earlier steps provide the foundation for subsequent progress. Thus, decisions about how to carry out a given step should not be finalized until prior steps have been thoroughly addressed.
However, these steps are meant to be adaptable, not rigid. Sensitivity to each program's unique context (for example, the program's history and organizational climate) is essential for sound evaluation. They are intended to serve as starting points around which community organizations can tailor an evaluation to best meet their needs.
Understanding and adhering to these basic steps will improve most evaluation efforts.
The second part of the framework is a basic set of standards to assess the quality of evaluation activities. There are 30 specific standards, organized into the following four groups:
These standards help answer the question, "Will this evaluation be a 'good' evaluation?" They are recommended as the initial criteria by which to judge the quality of the program evaluation efforts.
Stakeholders are people or organizations that have something to gain or lose from what will be learned from an evaluation, and also in what will be done with that knowledge. Evaluation cannot be done in isolation. Almost everything done in community health and development work involves partnerships - alliances among different organizations, board members, those affected by the problem, and others. Therefore, any serious effort to evaluate a program must consider the different values held by the partners. Stakeholders must be part of the evaluation to ensure that their unique perspectives are understood. When stakeholders are not appropriately involved, evaluation findings are likely to be ignored, criticized, or resisted.
However, if they are part of the process, people are likely to feel a good deal of ownership for the evaluation process and results. They will probably want to develop it, defend it, and make sure that the evaluation really works.
That's why this evaluation cycle begins by engaging stakeholders. Once involved, these people will help to carry out each of the steps that follows.
Likewise, individuals or groups who could be adversely or inadvertently affected by changes arising from the evaluation have a right to be engaged. For example, it is important to include those who would be affected if program services were expanded, altered, limited, or ended as a result of the evaluation.
The amount and type of stakeholder involvement will be different for each program evaluation. For instance, stakeholders can be directly involved in designing and conducting the evaluation. They can be kept informed about progress of the evaluation through periodic meetings, reports, and other means of communication.
It may be helpful, when working with a group such as this, to develop an explicit process to share power and resolve conflicts. This may help avoid overemphasis of values held by any specific stakeholder.
A program description is a summary of the intervention being evaluated. It should explain what the program is trying to accomplish and how it tries to bring about those changes. The description will also illustrate the program's core components and elements, its ability to make changes, its stage of development, and how the program fits into the larger organizational and community environment.
How a program is described sets the frame of reference for all future decisions about its evaluation. For example, if a program is described as, "attempting to strengthen enforcement of existing laws that discourage underage drinking," the evaluation might be very different than if it is described as, "a program to reduce drunk driving by teens." Also, the description allows members of the group to compare the program to other similar efforts, and it makes it easier to figure out what parts of the program brought about what effects.
Moreover, different stakeholders may have different ideas about what the program is supposed to achieve and why. For example, a program to reduce teen pregnancy may have some members who believe this means only increasing access to contraceptives, and other members who believe it means only focusing on abstinence.
Evaluations done without agreement on the program definition aren't likely to be very useful. In many cases, the process of working with stakeholders to develop a clear and logical program description will bring benefits long before data are available to measure program effectiveness.
Statement of need
A statement of need describes the problem, goal, or opportunity that the program addresses; it also begins to imply what the program will do in response. Important features to note regarding a program's need are: the nature of the problem or goal, who is affected, how big it is, and whether (and how) it is changing.
Expectations
Expectations are the program's intended results. They describe what the program has to accomplish to be considered successful. For most programs, the accomplishments exist on a continuum (first, we want to accomplish X. then, we want to do Y. ). Therefore, they should be organized by time ranging from specific (and immediate) to broad (and longer-term) consequences. For example, a program's vision, mission, goals, and objectives, all represent varying levels of specificity about a program's expectations.
Activities
Activities are everything the program does to bring about changes. Describing program components and elements permits specific strategies and actions to be listed in logical sequence. This also shows how different program activities, such as education and enforcement, relate to one another. Describing program activities also provides an opportunity to distinguish activities that are the direct responsibility of the program from those that are conducted by related programs or partner organizations. Things outside of the program that may affect its success, such as harsher laws punishing businesses that sell alcohol to minors, can also be noted.
Resources
Resources include the time, talent, equipment, information, money, and other assets available to conduct program activities. Reviewing the resources a program has tells a lot about the amount and intensity of its services. It may also point out situations where there is a mismatch between what the group wants to do and the resources available to carry out these activities. Understanding program costs is a necessity to assess the cost-benefit ratio as part of the evaluation.
Stage of development
A program's stage of development reflects its maturity. All community health and development programs mature and change over time. People who conduct evaluations, as well as those who use their findings, need to consider the dynamic nature of programs. For example, a new program that just received its first grant may differ in many respects from one that has been running for over a decade.
At least three phases of development are commonly recognized: planning, implementation, and effects or outcomes. In the planning stage, program activities are untested and the goal of evaluation is to refine plans as much as possible. In the implementation phase, program activities are being field tested and modified; the goal of evaluation is to see what happens in the "real world" and to improve operations. In the effects stage, enough time has passed for the program's effects to emerge; the goal of evaluation is to identify and understand the program's results, including those that were unintentional.
Context
A description of the program's context considers the important features of the environment in which the program operates. This includes understanding the area's history, geography, politics, and social and economic conditions, and also what other organizations have done. A realistic and responsive evaluation is sensitive to a broad range of potential influences on the program. An understanding of the context lets users interpret findings accurately and assess their generalizability. For example, a program to improve housing in an inner-city neighborhood might have been a tremendous success, but would likely not work in a small town on the other side of the country without significant adaptation.
Logic model
A logic model synthesizes the main program elements into a picture of how the program is supposed to work. It makes explicit the sequence of events that are presumed to bring about change. Often this logic is displayed in a flow-chart, map, or table to portray the sequence of steps leading to program results.
Creating a logic model allows stakeholders to improve and focus program direction. It reveals assumptions about conditions for program effectiveness and provides a frame of reference for one or more evaluations of the program. A detailed logic model can also be a basis for estimating the program's effect on endpoints that are not directly measured. For example, it may be possible to estimate the rate of reduction in disease from a known number of persons experiencing the intervention if there is prior knowledge about its effectiveness.
The breadth and depth of a program description will vary for each program evaluation. And so, many different activities may be part of developing that description. For instance, multiple sources of information could be pulled together to construct a well-rounded description. The accuracy of an existing program description could be confirmed through discussion with stakeholders. Descriptions of what's going on could be checked against direct observation of activities in the field. A narrow program description could be fleshed out by addressing contextual factors (such as staff turnover, inadequate resources, political pressures, or strong community participation) that may affect program performance.
By focusing the evaluation design, we mean doing advance planning about where the evaluation is headed, and what steps it will take to get there. It isn't possible or useful for an evaluation to try to answer all questions for all stakeholders; there must be a focus. A well-focused plan is a safeguard against using time and resources inefficiently.
Depending on what you want to learn, some types of evaluation will be better suited than others. However, once data collection begins, it may be difficult or impossible to change what you are doing, even if it becomes obvious that other methods would work better. A thorough plan anticipates intended uses and creates an evaluation strategy with the greatest chance to be useful, feasible, proper, and accurate.
Purpose
Purpose refers to the general intent of the evaluation. A clear purpose serves as the basis for the design, methods, and use of the evaluation. Taking time to articulate an overall purpose will stop your organization from making uninformed decisions about how the evaluation should be conducted and used.
There are at least four general purposes for which a community group might conduct an evaluation:
Users
Users are the specific individuals who will receive evaluation findings. They will directly experience the consequences of inevitable trade-offs in the evaluation process. For example, a trade-off might be having a relatively modest evaluation to fit the budget with the outcome that the evaluation results will be less certain than they would be for a full-scale evaluation. Because they will be affected by these tradeoffs, intended users have a right to participate in choosing a focus for the evaluation. An evaluation designed without adequate user involvement in selecting the focus can become a misguided and irrelevant exercise. By contrast, when users are encouraged to clarify intended uses, priority questions, and preferred methods, the evaluation is more likely to focus on things that will inform (and influence) future actions.
Uses
Uses describe what will be done with what is learned from the evaluation. There is a wide range of potential uses for program evaluation. Generally speaking, the uses fall in the same four categories as the purposes listed above: to gain insight, improve how things get done, determine what the effects of the program are, and affect participants. The following list gives examples of uses in each category.
Questions
The evaluation needs to answer specific questions. Drafting questions encourages stakeholders to reveal what they believe the evaluation should answer. That is, what questions are more important to stakeholders? The process of developing evaluation questions further refines the focus of the evaluation.
Methods
The methods available for an evaluation are drawn from behavioral science and social research and development. Three types of methods are commonly recognized. They are experimental, quasi-experimental, and observational or case study designs. Experimental designs use random assignment to compare the effect of an intervention between otherwise equivalent groups (for example, comparing a randomly assigned group of students who took part in an after-school reading program with those who didn't). Quasi-experimental methods make comparisons between groups that aren't equal (e.g. program participants vs. those on a waiting list) or use of comparisons within a group over time, such as in an interrupted time series in which the intervention may be introduced sequentially across different individuals, groups, or contexts. Observational or case study methods use comparisons within a group to describe and explain what happens (e.g., comparative case studies with multiple communities).
No design is necessarily better than another. Evaluation methods should be selected because they provide the appropriate information to answer stakeholders' questions, not because they are familiar, easy, or popular. The choice of methods has implications for what will count as evidence, how that evidence will be gathered, and what kind of claims can be made. Because each method option has its own biases and limitations, evaluations that mix methods are generally more robust.
Over the course of an evaluation, methods may need to be revised or modified. Circumstances that make a particular approach useful can change. For example, the intended use of the evaluation could shift from discovering how to improve the program to helping decide about whether the program should continue or not. Thus, methods may need to be adapted or redesigned to keep the evaluation on track.
Agreements
Agreements summarize the evaluation procedures and clarify everyone's roles and responsibilities. An agreement describes how the evaluation activities will be implemented. Elements of an agreement include statements about the intended purpose, users, uses, and methods, as well as a summary of the deliverables, those responsible, a timeline, and budget.
The formality of the agreement depends upon the relationships that exist between those involved. For example, it may take the form of a legal contract, a detailed protocol, or a simple memorandum of understanding. Regardless of its formality, creating an explicit agreement provides an opportunity to verify the mutual understanding needed for a successful evaluation. It also provides a basis for modifying procedures if that turns out to be necessary.
As you can see, focusing the evaluation design may involve many activities. For instance, both supporters and skeptics of the program could be consulted to ensure that the proposed evaluation questions are politically viable. A menu of potential evaluation uses appropriate for the program's stage of development could be circulated among stakeholders to determine which is most compelling. Interviews could be held with specific intended users to better understand their information needs and timeline for action. Resource requirements could be reduced when users are willing to employ more timely but less precise evaluation methods.
Credible evidence is the raw material of a good evaluation. The information learned should be seen by stakeholders as believable, trustworthy, and relevant to answer their questions. This requires thinking broadly about what counts as "evidence." Such decisions are always situational; they depend on the question being posed and the motives for asking it. For some questions, a stakeholder's standard for credibility could demand having the results of a randomized experiment. For another question, a set of well-done, systematic observations such as interactions between an outreach worker and community residents, will have high credibility. The difference depends on what kind of information the stakeholders want and the situation in which it is gathered.
Context matters! In some situations, it may be necessary to consult evaluation specialists. This may be especially true if concern for data quality is especially high. In other circumstances, local people may offer the deepest insights. Regardless of their expertise, however, those involved in an evaluation should strive to collect information that will convey a credible, well-rounded picture of the program and its efforts.
Having credible evidence strengthens the evaluation results as well as the recommendations that follow from them. Although all types of data have limitations, it is possible to improve an evaluation's overall credibility. One way to do this is by using multiple procedures for gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data. Encouraging participation by stakeholders can also enhance perceived credibility. When stakeholders help define questions and gather data, they will be more likely to accept the evaluation's conclusions and to act on its recommendations.
Indicators
Indicators translate general concepts about the program and its expected effects into specific, measurable parts.
Examples of indicators include:
Indicators should address the criteria that will be used to judge the program. That is, they reflect the aspects of the program that are most meaningful to monitor. Several indicators are usually needed to track the implementation and effects of a complex program or intervention.
One way to develop multiple indicators is to create a "balanced scorecard," which contains indicators that are carefully selected to complement one another. According to this strategy, program processes and effects are viewed from multiple perspectives using small groups of related indicators. For instance, a balanced scorecard for a single program might include indicators of how the program is being delivered; what participants think of the program; what effects are observed; what goals were attained; and what changes are occurring in the environment around the program.
Another approach to using multiple indicators is based on a program logic model, such as we discussed earlier in the section. A logic model can be used as a template to define a full spectrum of indicators along the pathway that leads from program activities to expected effects. For each step in the model, qualitative and/or quantitative indicators could be developed.
Indicators can be broad-based and don't need to focus only on a program's long -term goals. They can also address intermediary factors that influence program effectiveness, including such intangible factors as service quality, community capacity, or inter -organizational relations. Indicators for these and similar concepts can be created by systematically identifying and then tracking markers of what is said or done when the concept is expressed.
In the course of an evaluation, indicators may need to be modified or new ones adopted. Also, measuring program performance by tracking indicators is only one part of evaluation, and shouldn't be confused as a basis for decision making in itself. There are definite perils to using performance indicators as a substitute for completing the evaluation process and reaching fully justified conclusions. For example, an indicator, such as a rising rate of unemployment, may be falsely assumed to reflect a failing program when it may actually be due to changing environmental conditions that are beyond the program's control.
Sources
Sources of evidence in an evaluation may be people, documents, or observations. More than one source may be used to gather evidence for each indicator. In fact, selecting multiple sources provides an opportunity to include different perspectives about the program and enhances the evaluation's credibility. For instance, an inside perspective may be reflected by internal documents and comments from staff or program managers; whereas clients and those who do not support the program may provide different, but equally relevant perspectives. Mixing these and other perspectives provides a more comprehensive view of the program or intervention.
The criteria used to select sources should be clearly stated so that users and other stakeholders can interpret the evidence accurately and assess if it may be biased. In addition, some sources provide information in narrative form (for example, a person's experience when taking part in the program) and others are numerical (for example, how many people were involved in the program). The integration of qualitative and quantitative information can yield evidence that is more complete and more useful, thus meeting the needs and expectations of a wider range of stakeholders.
Quality
Quality refers to the appropriateness and integrity of information gathered in an evaluation. High quality data are reliable and informative. It is easier to collect if the indicators have been well defined. Other factors that affect quality may include instrument design, data collection procedures, training of those involved in data collection, source selection, coding, data management, and routine error checking. Obtaining quality data will entail tradeoffs (e.g. breadth vs. depth); stakeholders should decide together what is most important to them. Because all data have limitations, the intent of a practical evaluation is to strive for a level of quality that meets the stakeholders' threshold for credibility.
Quantity
Quantity refers to the amount of evidence gathered in an evaluation. It is necessary to estimate in advance the amount of information that will be required and to establish criteria to decide when to stop collecting data - to know when enough is enough. Quantity affects the level of confidence or precision users can have - how sure we are that what we've learned is true. It also partly determines whether the evaluation will be able to detect effects. All evidence collected should have a clear, anticipated use.
Logistics
By logistics, we mean the methods, timing, and physical infrastructure for gathering and handling evidence. People and organizations also have cultural preferences that dictate acceptable ways of asking questions and collecting information, including who would be perceived as an appropriate person to ask the questions. For example, some participants may be unwilling to discuss their behavior with a stranger, whereas others are more at ease with someone they don't know. Therefore, the techniques for gathering evidence in an evaluation must be in keeping with the cultural norms of the community. Data collection procedures should also ensure that confidentiality is protected.
The process of justifying conclusions recognizes that evidence in an evaluation does not necessarily speak for itself. Evidence must be carefully considered from a number of different stakeholders' perspectives to reach conclusions that are well -substantiated and justified. Conclusions become justified when they are linked to the evidence gathered and judged against agreed-upon values set by the stakeholders. Stakeholders must agree that conclusions are justified in order to use the evaluation results with confidence.
Standards
Standards reflect the values held by stakeholders about the program. They provide the basis to make program judgments. The use of explicit standards for judgment is fundamental to sound evaluation. In practice, when stakeholders articulate and negotiate their values, these become the standards to judge whether a given program's performance will, for instance, be considered "successful," "adequate," or "unsuccessful."
Analysis and synthesis
Analysis and synthesis are methods to discover and summarize an evaluation's findings. They are designed to detect patterns in evidence, either by isolating important findings (analysis) or by combining different sources of information to reach a larger understanding (synthesis). Mixed method evaluations require the separate analysis of each evidence element, as well as a synthesis of all sources to examine patterns that emerge. Deciphering facts from a given body of evidence involves deciding how to organize, classify, compare, and display information. These decisions are guided by the questions being asked, the types of data available, and especially by input from stakeholders and primary intended users.
Interpretation
Interpretation is the effort to figure out what the findings mean. Uncovering facts about a program's performance isn't enough to make conclusions. The facts must be interpreted to understand their practical significance. For example, saying, "15 % of the people in our area witnessed a violent act last year," may be interpreted differently depending on the situation. For example, if 50% of community members had watched a violent act in the last year when they were surveyed five years ago, the group can suggest that, while still a problem, things are getting better in the community. However, if five years ago only 7% of those surveyed said the same thing, community organizations may see this as a sign that they might want to change what they are doing. In short, interpretations draw on information and perspectives that stakeholders bring to the evaluation. They can be strengthened through active participation or interaction with the data and preliminary explanations of what happened.
Judgements
Judgments are statements about the merit, worth, or significance of the program. They are formed by comparing the findings and their interpretations against one or more selected standards. Because multiple standards can be applied to a given program, stakeholders may reach different or even conflicting judgments. For instance, a program that increases its outreach by 10% from the previous year may be judged positively by program managers, based on standards of improved performance over time. Community members, however, may feel that despite improvements, a minimum threshold of access to services has still not been reached. Their judgment, based on standards of social equity, would therefore be negative. Conflicting claims about a program's quality, value, or importance often indicate that stakeholders are using different standards or values in making judgments. This type of disagreement can be a catalyst to clarify values and to negotiate the appropriate basis (or bases) on which the program should be judged.
Recommendations
Recommendations are actions to consider as a result of the evaluation. Forming recommendations requires information beyond just what is necessary to form judgments. For example, knowing that a program is able to increase the services available to battered women doesn't necessarily translate into a recommendation to continue the effort, particularly when there are competing priorities or other effective alternatives. Thus, recommendations about what to do with a given intervention go beyond judgments about a specific program's effectiveness.
If recommendations aren't supported by enough evidence, or if they aren't in keeping with stakeholders' values, they can really undermine an evaluation's credibility. By contrast, an evaluation can be strengthened by recommendations that anticipate and react to what users will want to know.
Justifying conclusions in an evaluation is a process that involves different possible steps. For instance, conclusions could be strengthened by searching for alternative explanations from the ones you have chosen, and then showing why they are unsupported by the evidence. When there are different but equally well supported conclusions, each could be presented with a summary of their strengths and weaknesses. Techniques to analyze, synthesize, and interpret findings might be agreed upon before data collection begins.
It is naive to assume that lessons learned in an evaluation will necessarily be used in decision making and subsequent action. Deliberate effort on the part of evaluators is needed to ensure that the evaluation findings will be used appropriately. Preparing for their use involves strategic thinking and continued vigilance in looking for opportunities to communicate and influence. Both of these should begin in the earliest stages of the process and continue throughout the evaluation.
Design
Design refers to how the evaluation's questions, methods, and overall processes are constructed. As discussed in the third step of this framework (focusing the evaluation design), the evaluation should be organized from the start to achieve specific agreed-upon uses. Having a clear purpose that is focused on the use of what is learned helps those who will carry out the evaluation to know who will do what with the findings. Furthermore, the process of creating a clear design will highlight ways that stakeholders, through their many contributions, can improve the evaluation and facilitate the use of the results.
Preparation
Preparation refers to the steps taken to get ready for the future uses of the evaluation findings. The ability to translate new knowledge into appropriate action is a skill that can be strengthened through practice. In fact, building this skill can itself be a useful benefit of the evaluation. It is possible to prepare stakeholders for future use of the results by discussing how potential findings might affect decision making.
For example, primary intended users and other stakeholders could be given a set of hypothetical results and asked what decisions or actions they would make on the basis of this new knowledge. If they indicate that the evidence presented is incomplete or irrelevant and that no action would be taken, then this is an early warning sign that the planned evaluation should be modified. Preparing for use also gives stakeholders more time to explore both positive and negative implications of potential results and to identify different options for program improvement.
Feedback
Feedback is the communication that occurs among everyone involved in the evaluation. Giving and receiving feedback creates an atmosphere of trust among stakeholders; it keeps an evaluation on track by keeping everyone informed about how the evaluation is proceeding. Primary intended users and other stakeholders have a right to comment on evaluation decisions. From a standpoint of ensuring use, stakeholder feedback is a necessary part of every step in the evaluation. Obtaining valuable feedback can be encouraged by holding discussions during each step of the evaluation and routinely sharing interim findings, provisional interpretations, and draft reports.
Follow-up
Follow-up refers to the support that many users need during the evaluation and after they receive evaluation findings. Because of the amount of effort required, reaching justified conclusions in an evaluation can seem like an end in itself. It is not. Active follow-up may be necessary to remind users of the intended uses of what has been learned. Follow-up may also be required to stop lessons learned from becoming lost or ignored in the process of making complex or political decisions. To guard against such oversight, it may be helpful to have someone involved in the evaluation serve as an advocate for the evaluation's findings during the decision -making phase.
Facilitating the use of evaluation findings also carries with it the responsibility to prevent misuse. Evaluation results are always bounded by the context in which the evaluation was conducted. Some stakeholders, however, may be tempted to take results out of context or to use them for different purposes than what they were developed for. For instance, over-generalizing the results from a single case study to make decisions that affect all sites in a national program is an example of misuse of a case study evaluation.
Similarly, program opponents may misuse results by overemphasizing negative findings without giving proper credit for what has worked. Active follow-up can help to prevent these and other forms of misuse by ensuring that evidence is only applied to the questions that were the central focus of the evaluation.
Dissemination
Dissemination is the process of communicating the procedures or the lessons learned from an evaluation to relevant audiences in a timely, unbiased, and consistent fashion. Like other elements of the evaluation, the reporting strategy should be discussed in advance with intended users and other stakeholders. Planning effective communications also requires considering the timing, style, tone, message source, vehicle, and format of information products. Regardless of how communications are constructed, the goal for dissemination is to achieve full disclosure and impartial reporting.
Along with the uses for evaluation findings, there are also uses that flow from the very process of evaluating. These "process uses" should be encouraged. The people who take part in an evaluation can experience profound changes in beliefs and behavior. For instance, an evaluation challenges staff members to act differently in what they are doing, and to question assumptions that connect program activities with intended effects.
Evaluation also prompts staff to clarify their understanding of the goals of the program. This greater clarity, in turn, helps staff members to better function as a team focused on a common end. In short, immersion in the logic, reasoning, and values of evaluation can have very positive effects, such as basing decisions on systematic judgments instead of on unfounded assumptions.
Additional process uses for evaluation include:
There are standards to assess whether all of the parts of an evaluation are well -designed and working to their greatest potential. The Joint Committee on Educational Evaluation developed "The Program Evaluation Standards" for this purpose. These standards, designed to assess evaluations of educational programs, are also relevant for programs and interventions related to community health and development.
The program evaluation standards make it practical to conduct sound and fair evaluations. They offer well-supported principles to follow when faced with having to make tradeoffs or compromises. Attending to the standards can guard against an imbalanced evaluation, such as one that is accurate and feasible, but isn't very useful or sensitive to the context. Another example of an imbalanced evaluation is one that would be genuinely useful, but is impossible to carry out.
The following standards can be applied while developing an evaluation design and throughout the course of its implementation. Remember, the standards are written as guiding principles, not as rigid rules to be followed in all situations.
The utility standards are:
The feasibility standards are to ensure that the evaluation makes sense - that the steps that are planned are both viable and pragmatic.
The feasibility standards are:
The propriety standards ensure that the evaluation is an ethical one, conducted with regard for the rights and interests of those involved. The eight propriety standards follow.
The accuracy standards ensure that the evaluation findings are considered correct.
There are 12 accuracy standards:
There is an ever-increasing agreement on the worth of evaluation; in fact, doing so is often required by funders and other constituents. So, community health and development professionals can no longer question whether or not to evaluate their programs. Instead, the appropriate questions are:
The framework for program evaluation helps answer these questions by guiding users to select evaluation strategies that are useful, feasible, proper, and accurate.
To use this framework requires quite a bit of skill in program evaluation. In most cases there are multiple stakeholders to consider, the political context may be divisive, steps don't always follow a logical order, and limited resources may make it difficult to take a preferred course of action. An evaluator's challenge is to devise an optimal strategy, given the conditions she is working under. An optimal strategy is one that accomplishes each step in the framework in a way that takes into account the program context and is able to meet or exceed the relevant standards.
This framework also makes it possible to respond to common concerns about program evaluation. For instance, many evaluations are not undertaken because they are seen as being too expensive. The cost of an evaluation, however, is relative; it depends upon the question being asked and the level of certainty desired for the answer. A simple, low-cost evaluation can deliver information valuable for understanding and improvement.
Rather than discounting evaluations as a time-consuming sideline, the framework encourages evaluations that are timed strategically to provide necessary feedback. This makes it possible to make evaluation closely linked with everyday practices.
Another concern centers on the perceived technical demands of designing and conducting an evaluation. However, the practical approach endorsed by this framework focuses on questions that can improve the program.
Finally, the prospect of evaluation troubles many staff members because they perceive evaluation methods as punishing ("They just want to show what we're doing wrong."), exclusionary ("Why aren't we part of it? We're the ones who know what's going on."), and adversarial ("It's us against them.") The framework instead encourages an evaluation approach that is designed to be helpful and engages all interested stakeholders in a process that welcomes their participation.
Evaluation is a powerful strategy for distinguishing programs and interventions that make a difference from those that don't. It is a driving force for developing and adapting sound strategies, improving existing programs, and demonstrating the results of investments in time and other resources. It also helps determine if what is being done is worth the cost.
This recommended framework for program evaluation is both a synthesis of existing best practices and a set of standards for further improvement. It supports a practical approach to evaluation based on steps and standards that can be applied in almost any setting. Because the framework is purposefully general, it provides a stable guide to design and conduct a wide range of evaluation efforts in a variety of specific program areas. The framework can be used as a template to create useful evaluation plans to contribute to understanding and improvement. The Magenta Book - Guidance for Evaluation provides additional information on requirements for good evaluation, and some straightforward steps to make a good evaluation of an intervention more feasible, read The Magenta Book - Guidance for Evaluation.